Polynomial Regression
Polynomial Regression
If your data points clearly will not fit a linear regression (a straight line through all data points), it might be ideal for polynomial regression.
Polynomial regression, like linear regression, uses the relationship between the variables x and y to find the best way to draw a line through the data points.
How Does it Work?
Python has methods for finding a relationship between data-points and to draw a line of polynomial regression. We will show you how to use these methods instead of going through the mathematic formula.
In the example below, we have registered 18 cars as they were passing a certain tollbooth.
We have registered the car's speed, and the time of day (hour) the passing occurred.
The x-axis represents the hours of the day and the y-axis represents the speed:
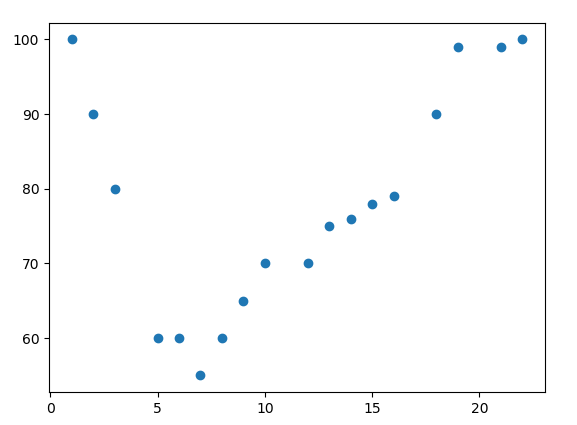
Example
Start by drawing a scatter plot:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt:
x = [1,2,3,5,6,7,8,9,10,12,13,14,15,16,18,19,21,22]
y = [100,90,80,60,60,55,60,65,70,70,75,76,78,79,90,99,99,100]
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.show()
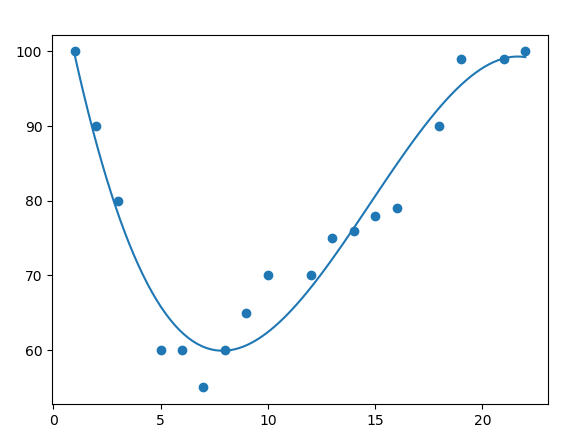
Example
Import numpy and matplotlib then draw the line of Polynomial Regression:
import numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = [1,2,3,5,6,7,8,9,10,12,13,14,15,16,18,19,21,22]
y = [100,90,80,60,60,55,60,65,70,70,75,76,78,79,90,99,99,100]
mymodel = numpy.poly1d(numpy.polyfit(x, y, 3))
myline = numpy.linspace(1, 22, 100)
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.plot(myline, mymodel(myline))
plt.show()
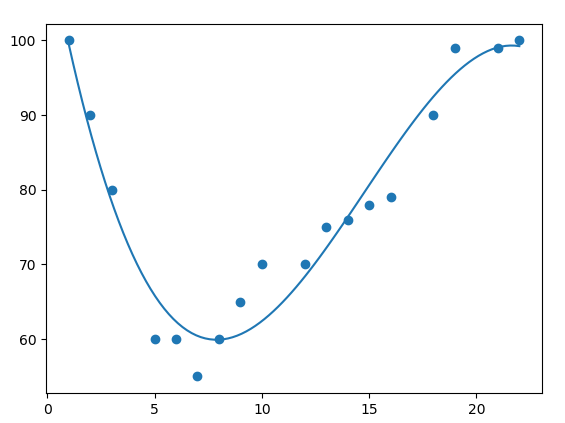
Example Explained
Import the modules you need.
import numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Create the arrays that represent the values of the x and y axis:
x = [1,2,3,5,6,7,8,9,10,12,13,14,15,16,18,19,21,22]
y = [100,90,80,60,60,55,60,65,70,70,75,76,78,79,90,99,99,100]
NumPy has a method that lets us make a polynomial model:
mymodel = numpy.poly1d(numpy.polyfit(x, y, 3))
Then specify how the line will display, we start at position 1, and end at position 22:
myline = numpy.linspace(1, 22, 100)
Draw the original scatter plot:
plt.scatter(x, y)
Draw the line of polynomial regression:
plt.plot(myline, mymodel(myline))
Display the diagram:
plt.show()
R-Squared
It is important to know how well the relationship between the values of the x- and y-axis is, if there are no relationship the polynomial regression can not be used to predict anything.
The relationship is measured with a value called the r-squared.
The r-squared value ranges from 0 to 1, where 0 means no relationship, and 1 means 100% related.
Python and the Sklearn module will compute this value for you, all you have to do is feed it with the x and y arrays:
Example
How well does my data fit in a polynomial regression?
import numpy
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
x = [1,2,3,5,6,7,8,9,10,12,13,14,15,16,18,19,21,22]
y = [100,90,80,60,60,55,60,65,70,70,75,76,78,79,90,99,99,100]
mymodel = numpy.poly1d(numpy.polyfit(x, y, 3))
print(r2_score(y, mymodel(x)))