Learn Statistics Median
The median is a type of average value, which describes where the center of the data is located.
Median
The median is the middle value in a data set ordered from low to high.
Finding the Median
The median can only be calculated for numerical variables.
The formula for finding the middle value is:
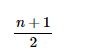
Where is the total number of observations.
If the total number of observations is an odd number, the formula gives a whole number and the value of this observation is the median.
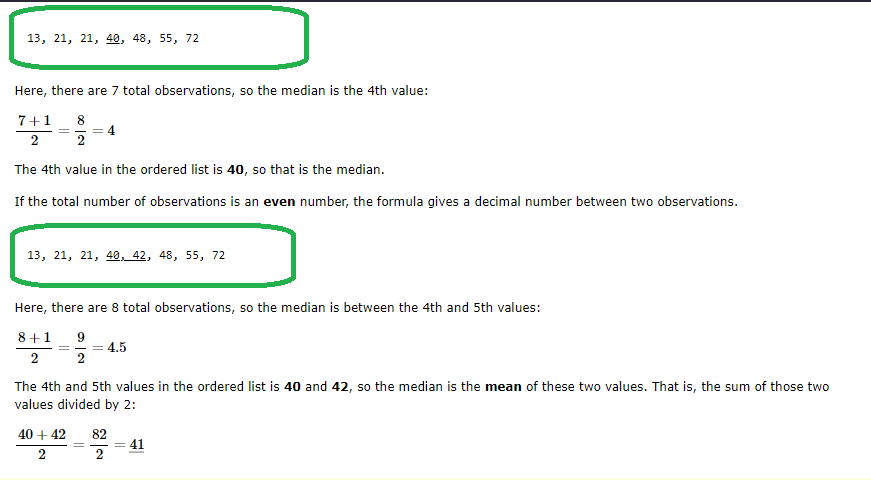
Note: It is important that the numbers are ordered before you can find the median.
Finding the Median with Programming
The median can easily be found with many programming languages.
Using software and programming to calculate statistics is more common for bigger sets of data, as finding it manually becomes difficult.
Example:
With Python use the NumPy library median() method to find the median of the values 13, 21, 21, 40, 42, 48, 55, 72:
import numpy
values = [13,21,21,40,42,48,55,72]
x = numpy.median(values)
print(x)
Example:
Use the R median() function to find the median of the values 13, 21, 21, 40, 42, 48, 55, 72:
values <- c(13,21,21,40,42,48,55,72)
median(values)